Why Do Low-Speed Vehicle Batteries Matter for Eco-Friendly Transportation
The shift towards eco-friendly transportation is increasingly shaping the automotive industry, particularly in the context of low-speed vehicles (LSVs). As cities worldwide aim to reduce their carbon emissions and promote sustainable urban mobility, the significance of Low-Speed Vehicle Batteries has come to the forefront. According to a report by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT), the adoption of LSVs can potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 30% in congested urban areas where speeds typically do not exceed 25 mph. This transition necessitates a reliable and efficient battery system that can support the unique operational demands of these vehicles.
As noted by Dr. Emily Green, a leading expert in battery technology at the Global Battery Alliance, "The development of advanced Low-Speed Vehicle Batteries is crucial not only for enhancing the electric driving experience but also for making substantial contributions to our global sustainability goals." With the right investment in research and development, these batteries can provide longer ranges, faster charging times, and improved safety, making LSVs an attractive alternative to conventional transportation. Consequently, fostering innovation in Low-Speed Vehicle Battery technology will play a pivotal role in ushering in a new era of eco-friendly transit solutions.

The Role of Low-Speed Vehicles in Sustainable Transportation
Low-speed vehicles (LSVs) are becoming an integral part of the sustainable transportation landscape, especially in urban settings where traditional vehicular traffic is often congested. These small electric or low-emission vehicles offer an eco-friendly alternative for short-distance travel, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), transportation contributes to nearly 24% of global CO2 emissions, and the increase in LSV usage could play a pivotal role in mitigating this impact. Additionally, a report from the U.S. Department of Transportation indicates that LSVs can reduce fuel consumption by up to 80% compared to conventional vehicles, making them a practical choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Tips: When considering incorporating LSVs into your transportation routine, evaluate your daily travel needs. If you're primarily making short trips within a community, an LSV may be an ideal solution that aligns with sustainable practices while also minimizing your carbon footprint.
In urban areas, LSVs alleviate the burden on transport infrastructure, require less parking space, and enhance mobility for residents. Their smaller size allows for easier navigation through crowded streets and their electrification contributes to improved air quality. The Sustainable Transportation Initiative reports that the adoption of LSVs can lead to a notable decrease in urban traffic congestion, promoting a healthier lifestyle and more accessible mobility options for all citizens.
Tips: To maximize the benefits of LSVs, consider promoting their use within your community by establishing designated lanes and charging stations, which can further incentivize eco-friendly transportation choices.
Why Do Low-Speed Vehicle Batteries Matter for Eco-Friendly Transportation - The Role of Low-Speed Vehicles in Sustainable Transportation
| Battery Type | Average Capacity (kWh) | Charging Time (hours) | Lifecycle (cycles) | Environmental Impact (CO2 kg/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | 6 | 8 | 300 | 0.6 |
| Lithium-Ion | 10 | 4 | 500 | 0.1 |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride | 7 | 6 | 400 | 0.3 |
| Solid-State | 12 | 3 | 1000 | 0.05 |
Key Components of Low-Speed Vehicle Batteries
Low-speed vehicle (LSV) batteries play a crucial role in promoting eco-friendly transportation solutions. These batteries are specially designed to provide the necessary power and efficiency for vehicles operating at lower speeds, typically in urban or residential settings. Key components of these batteries include lithium-ion technology, which offers high energy density, lightweight design, and extended lifecycle. This makes them particularly suitable for LSVs, as they help reduce the overall weight of the vehicle and, consequently, its energy consumption.
Another significant component is the battery management system (BMS), which ensures optimal performance and safety by monitoring the battery’s state of charge, temperature, and health. A well-designed BMS helps to maximize efficiency, prolong battery life, and safeguard against potential failures. This is vital for maintaining the reliability of LSVs, particularly for users who depend on these vehicles for daily transportation.
Tips: When choosing a battery for a low-speed vehicle, consider opting for lithium-ion options for their superior performance and sustainability. Regular maintenance of the battery and its management system can also enhance vehicle longevity and efficiency, so be sure to check battery connections and charge levels frequently. Lastly, always dispose of old batteries properly to minimize environmental impact and promote eco-friendly practices in transportation.
Environmental Impact of Low-Speed Vehicle Battery Technology
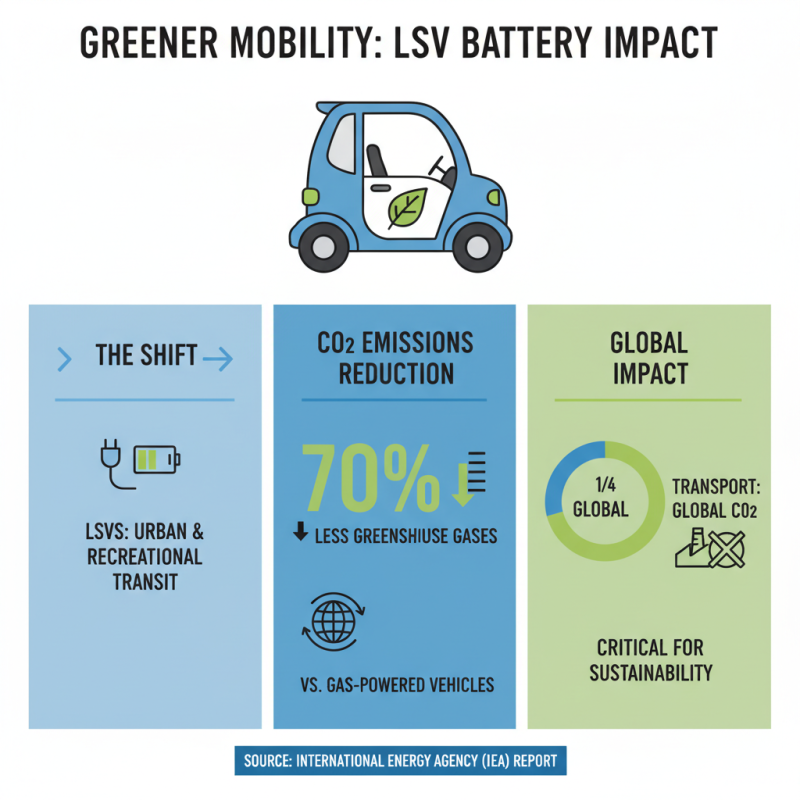
The environmental impact of low-speed vehicle (LSV) battery technology is significant, particularly as the demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions grows. LSVs, commonly used in urban areas and recreational settings, rely on advanced battery systems to operate efficiently and sustainably. A recent report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that the adoption of electric vehicles, including LSVs, could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles. This transition is critical as transportation accounts for nearly a quarter of global CO2 emissions.
Moreover, the type of battery technology employed in LSVs plays a crucial role in minimizing environmental harm. For instance, lithium-ion batteries are the predominant energy source due to their high energy density and long lifespan. However, concerns regarding lithium extraction and battery disposal have emerged. According to a study by the European Commission, the production and disposal of lithium-ion batteries can have a substantial environmental footprint if not managed properly. Advances in battery recycling technologies are essential; the industry aims to recover up to 95% of battery materials, thus reducing the need for new resource extraction and minimizing waste. Implementing sustainable practices across the lifecycle of LSV batteries is vital for achieving the broader goals of eco-friendly transportation and reducing the environmental impact of mobility solutions.
Challenges in Low-Speed Vehicle Battery Development
The development of batteries for low-speed vehicles (LSVs) presents unique challenges that are crucial for achieving eco-friendly transportation goals. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the growth of LSVs, particularly in urban areas, is expected to play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, the battery technology for such vehicles must overcome several hurdles to meet both performance and environmental standards.
One major challenge is the energy density of batteries used in LSVs. Unlike conventional electric vehicles, LSVs require batteries that can provide sufficient range while maintaining a compact size and weight. A recent report from the U.S. Department of Energy indicates that to achieve optimal efficiency, battery packs in LSVs need to enhance energy density from the current average of 150 Wh/kg to at least 250 Wh/kg. Additionally, the degradation rate of batteries used in lower speed operations can be higher due to frequent cycling and partial state of charge (SOC) operations, demanding innovations in battery chemistry and management systems.
Another significant obstacle involves the sustainability of battery materials. The transition to more eco-friendly alternatives is essential, yet the extraction and processing of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel can have negative environmental impacts. The McKinsey Global Institute highlights that developing a circular economy around battery materials—recycling existing batteries and deploying alternative materials—will be essential to mitigate these effects. Addressing these challenges is critical to ensuring that LSVs become a viable component of future sustainable transport networks.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Low-Speed Vehicle Batteries
As we strive for a greener future, low-speed vehicles (LSVs) are gaining traction as an eco-friendly transportation solution, especially in urban environments. These vehicles often rely on specialized batteries designed to maximize efficiency and minimize environmental impact. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards advanced battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur solutions, which promise increased energy density and reduced weight. According to a recent industry report, the global market for LSV batteries is projected to grow by over 30% annually, driven by demand for sustainable transport options and stricter emissions regulations.
In addition to technological advancements, there is an increasing emphasis on recycling and second-life applications for LSV batteries. Studies show that repurposing used batteries can reduce waste while extending their lifecycle, which is crucial for sustainability. The development of battery management systems (BMS) that optimize performance and lifespan will further enhance their eco-friendliness, making LSVs more appealing to both consumers and manufacturers.
**Tips:** To reduce your carbon footprint, consider utilizing LSVs for short commutes or errands. Staying informed about local recycling programs for used batteries can help contribute to a more sustainable ecosystem. Additionally, engaging with community initiatives promoting battery usage can create a more supportive environment for eco-friendly transportation solutions.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Low-Speed Vehicle Batteries
Related Posts
-
Finding the Ideal Manufacturer for Your Best Low-Speed Vehicle Battery Needs
-

Exploring the Future: How Power Storage Batteries Will Transform Renewable Energy
-

Top 5 Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Forklift Battery
-

Exploring the Future of Energy Storage with Lithium Polymer Batteries for Everyday Devices
-
Exploring the Future of Energy: The Role of Vacuum Circuit Breakers in Smart Grids
-

Top Strategies for Sourcing Best Rechargeable Lithium Batteries in Global Markets
